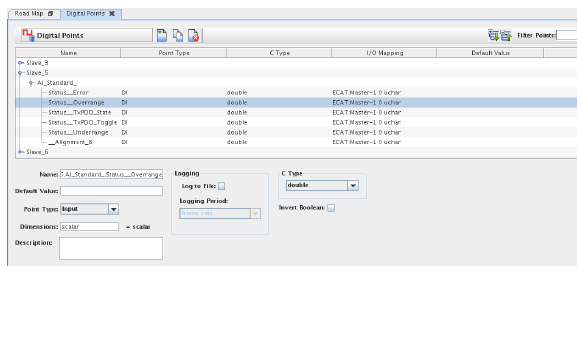
Manages I/O points in the current RTDB that can hold a boolean value.


Expands the hierarchy tree for all point names in the point table. Point names with periods in the names are hierarchical names and are displayed as a tree. A.ai000 and A.ai001 would display ai000 and ai001 as children of the A node.

Collapses the hierarchy tree for all point names in the point table to show just the top level nodes.
Displays in the points table only I/O points whose name matches the regular expression. See Regular Expressions.

Opens a short video clip that demonstrates the basic workflow of this form.

Opens this section of the manual.
List of all the digital I/O points in the Current RTDB. Click on a point to select it for editing, deletion, or copying.

Deletes the digital point selected in the Points Table. This button is enabled only if a point is selected in the Points Table. If you want to delete multiple points, Ctrl+Click to select the points of interest.

Creates a copy of the digital point selected in the Points Table. A unique name based on the original point name will be created for the new point. This button is enabled only if a point is selected in the Points Table. For more information, see Copying RTDB Points.

Creates a new point. A unique name will be created for the new point.
Name of the real-time database currently loaded for editing. See New/Select RTDB....

Commits all pending edits to the real-time host. See Apply .

Discards all pending edits.
Name of the selected point in the Points Table. Hierarchical names are shown “flat” with a period between each node of the hierarchy. Rename the point by simply typing in a new name.
Value that the selected point is set to at the beginning of a test run. If it is not specified (the field is blank), the value of the point at the beginning of a test run is undefined.
Directional type of the point.
The point may hold values read from an I/O device.
The point may hold values to be written to an I/O device.
The point may hold values read from or to be written to an I/O device.
Dimensionality of the I/O point. A “scalar” point can hold only a single value. An array may hold multiple values. The size of each dimension should be specified as an integer, and each dimension separated by the letter ‘x’. The total number of elements is displayed next to the field.
Most boards require only scalar points. See AI64SS:Stream for an example of a board that supports array points.
Brief description of the point for documentation purposes.
Enables periodic logging of values of the point.
Sets the period for logging for the point. The period can be the simulations’s frame rate or a rate chosen from the drop down list when the field is clicked on.
Internal representation of the point’s value as a ‘C’ variable.
Inverts the logical sense of the raw value read from the hardware.