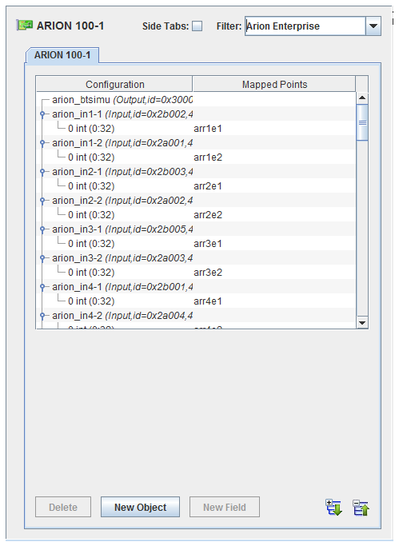
I/O points may be mapped to fields in named objects.

N/A
N/A
N/A

Expands the hierarchy tree showing board configuration.

Collapses the hierarchy tree showing the board configuration to show only the object nodes.

Adds a field to the selected object.
Adds an object definition.

Deletes the selected node and everything, including mappings, below it.
 To configure a new object, click on the New Object button. When an object is selected, the settings dialog below appears below the mapping table.
To configure a new object, click on the New Object button. When an object is selected, the settings dialog below appears below the mapping table.
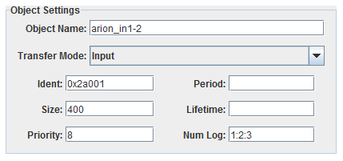
Name of the object.
I/O direction of the object.
Identifier between 0x64 and 0xffffff.
Size of the object. The size must be a multiple of four.
Priority of the object in the system. The priority must be between 0 and 15.
Period of the object in microseconds.
Duration of the object in microseconds.
Logical numbers of the equipment. The numbers must be between 1 and 63 and separated by colons.
 To create a new field, select an object and click on the New Field button.
To create a new field, select an object and click on the New Field button.
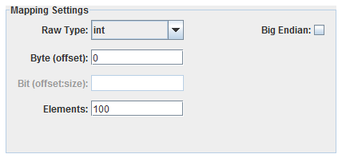
I/O points are mapped to specific fields of messages. All fields are specified with a byte offset into the shared memory region. Integer types can have an optional bit offset and size to specify bit field with the integer at that byte offset.
Single-bit integer fields can only be mapped to digital points. All other fields can only be mapped to analog points.
Specifies how to interpret the raw bits of the message field.
One-byte integer field.
Two-byte integer field.
Four-byte integer field.
Eight-byte integer field.
Four-byte floating point field.
Double-byte floating point field.
Field’s offset in the object in bytes.
Bit offset and size of a bit field within an integer. Leave blank to specify the entire integer. Bits are numbered from the high order bit of the 1-, 2-, 4-, or 8-byte block of the selected raw integer type. Which byte this bit is in is determined by the Big Endian setting. The offset is measured from the high order bit of the block to the high order bit of the field.
Number of elements of an array point this field will be mapped to. Leave blank or set to 1 to map to scalar points. Only points with at least this number of elements will be displayed on the right-hand side.
Interprets values as most significant byte first. This is the reverse of the default way data is handled on Intel x86 platforms.
To map a field to an I/O point, select a field on the left side of the I/O Mappings form, then click on a check box for an I/O point on the right side of the form. See I/O Mappings... for details.
Configuration tree.
I/O point(s) a field is mapped to.
To map a field to a channel, select a field on the left side of the I/O Mappings form, then click on a check box for an I/O point on the right side of the form. See I/O Mappings... for details.
|
ARINC429 | Baby LIN |
|