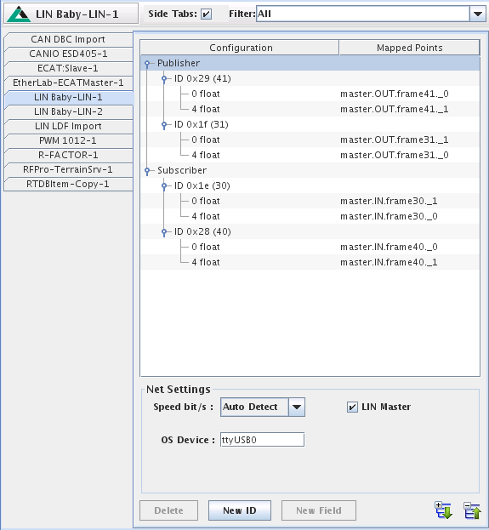
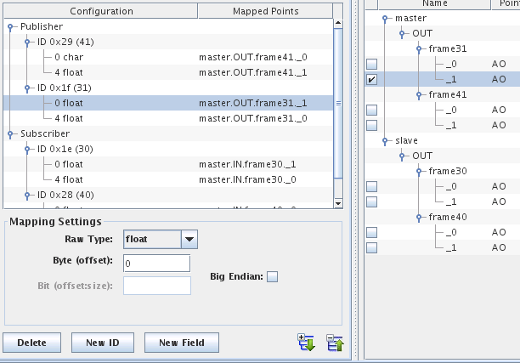
In LIN terminology, LIN nodes either publish a frame or subscribe to a frame. A frame publisher is responsible for generating the frame content while a frame subscriber is interested in receiving the specific frame to read its content. Master and slave nodes can both be publisher and subscriber of frames. However, there can only be a single publisher of a specific frame on a LIN network.
Buttons
Expand All 
Expands the hierarchy tree showing board configuration.
Collapse All 
Collapses the hierarchy tree showing the board configuration to show only the channel nodes.
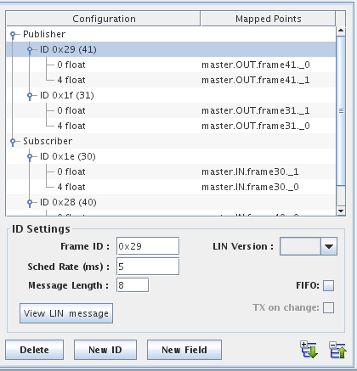
New ID
Adds a new LIN frame ID under the selected subscriber/publisher branch.
Delete
Deletes the selected frame ID and everything, including mappings, below it.
Speed bits/s
Select the speed at which this Baby LIN will connect to the LIN network. Auto detect can only be specified for a slave node.
LIN Master
Specify that this BabyLIN node is a LIN master.
OS Device
Specify the OS device to use for this specific Baby LIN device. Support to access the device is provided by the RedHawk kernel
via the usbserial device. Typical name for the OS device is /dev/ttyUSBx where x is a number starting at 0 for
the first Baby LIN device. This number may vary if you have other USB serial devices installed in your system. The ttyUSBx name must be unique for each
Baby LIN device, when multiple Baby LIN devices are being used.
Note: The device name can change if the system configuration changes. For example, when a new USB device is installed.