Overview
This example shows how to create RTDB (Real-time Database) and generate code for a Simulink model using the MLToolkit. The MLToolkit allows you to easily generate SimWB-compliant code from a Simulink model. It provides you the convenience of generating this code without modifying the Simulink model to include hardware-specific S-Function blocks. Instead, the software automatically inserts RTBD-access-specific blocks during code generation. Use the generated code to simulate the model in real time using SimWB, which supports a wide variety of I/Os for model simulation.
Content
Prerequisites
This example requires the MLToolkit. To confirm that this software is installed, open any Simulink model. The SimWB option must be visible in the menu bar. Before using the MLToolkit, you must start the Real-Time core process, cfgsrv, on the real-time host (Concurrent iHawk system). The cfgsrv process provides the runtime environment to run a Simulink model in real time. To start the cfgsrv process on the real-time host, run "service simwb start" in the terminal.
Specify Fixed-Step Solver for Model
This example uses autotrans_demo Simulink model (shipped with SimWB as an example), which models the automatic transmission controller of an automotive.
The autotrans_demo is based on the Simulink model sldemo_autotrans. For more information about this model, see
Automatic Transmission Controller
in Simulink documentation.
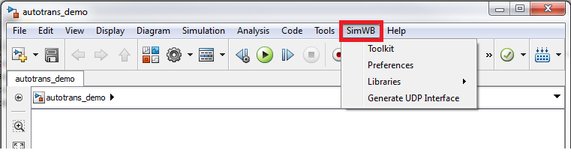
To generate code for a Simulink model, it must use a fixed-step solver. To specify a fixed-step solver, in the Simulink editor,
click Simulation > Model Configuration Parameters. In the Select pane (left-hand side) of the Configuration Parameters dialog box,
select Solver. In the Solver Options pane (right-hand side), select Fixed-step in the Type menu.
In the Fixed-step size box, enter 0.01.
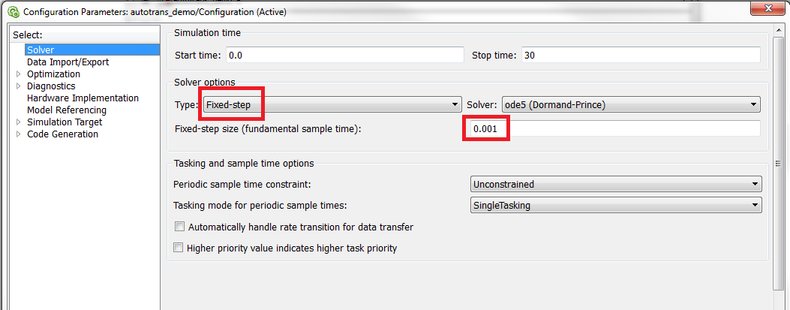
Prepare Signals of Interest in Simulink Model
To access signals in a Simulink model in real time using external hardware, ensure that these signals are connected to source
(inputs) or sink (outputs) blocks. These blocks are mapped to RTDB inputs/outputs.
If necessary, add the relevant blocks to the model. Specify names for these source/sink blocks that are valid C variable names.
Block names that contain spaces cannot be included in the real-time database. So, you must eliminate spaces from the names of
blocks of interest.
For example, by naming the input/output blocks with a prefix "SW", MLToolkit can pick up these blocks with regular expression "^SW" (starts with "SW") and
map these blocks to RTDB input/output accordingly.
Connect to the Real-time Host
Open the MLToolkit GUI. In the menu bar of the Simulink Editor for the model, click SimWB > Toolkit. In the Simulator Access tab, specify the following:
- Host Name - Name of the real-time host or IP address of the computer running the cfgsrv process (for example, 192.168.0.1)
- User Name, Password - Name and password of authorized user of RTDB
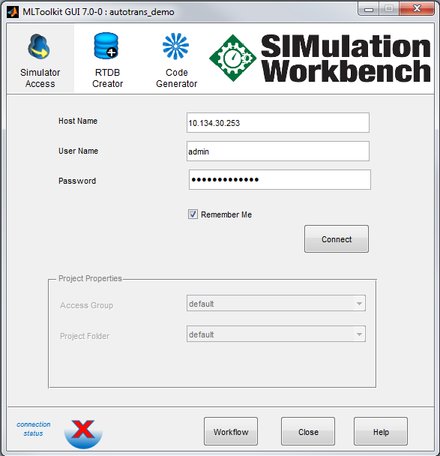
Click Connect. When successfully connected to the real-time host, the connection status icon change from
 to
to 
In the Project Properties pane, use the default values for Access Group and Project Folder.
Create RTDB
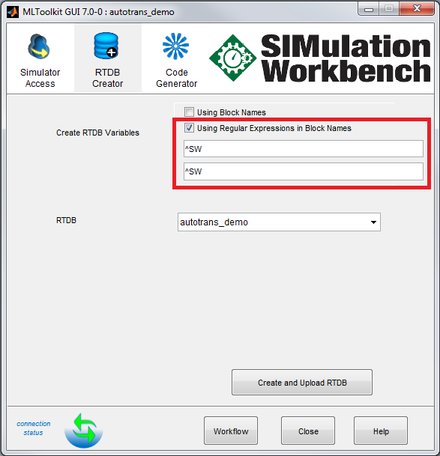
Click the RTDB Creator tab. Specify the following:
- Create RTDB Variables - Select the Using Regular Expressions in Block Names check box. Use the default values for the boxes that specify the regular expression values for the source and sink names.
- RTDB - Enter autotrans_demo. Typically, you specify the model or project name in this field.
A text file, signal.db, is created in the current folder. This file contains the RTDB variable definitions. The software uploads this file to the real-time host. So, when you use the SIMulation Workbench Control Center after generating the code, this model is available in the GUI.
Generate SimWB-Compliant Code
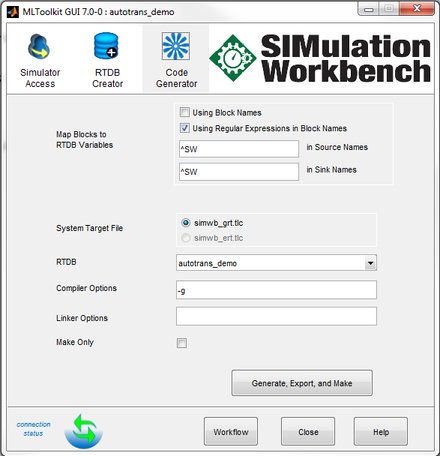
Click the Code Generator tab. Specify the following:
- Map Blocks to RTDB Variables - Use the same options as in the RTDB Creator tab.
- System Target File - Use the default option, simwb_grt.tlc.
- RTDB - Select autotrans_demo from the list. This is the RTDB name specified in the RTDB Creator tab. If autotrans_demo is not available in the list, the RTDB creation was unsuccessful.
- Compiler Options - Use the default value, -g.
- Linker Options - Use the default value, an empty string.
- Make Only - Use the default option, unselect this check box.
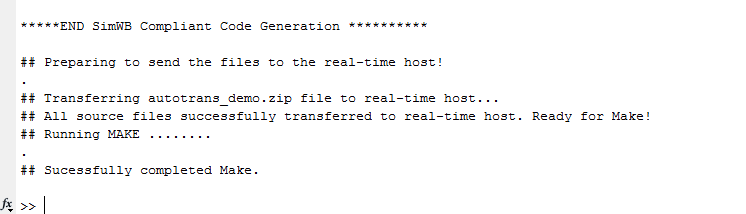
Click Generate, Export, and Make. The software generates SimWB-compliant code and a real-time executable, and uploads the same to the real-time host. The following image shows a snippet of the generated output from MATLAB command window.
The MLToolkit checks if the model is compliant with the selected RTDB before it generates SimWB-compliant code.
The check ensures that source and sink blocks in the model uniquely map to variables in the RTDB.
A block maps to an RTDB variable when they have the same name, data type, and dimension.
The model must pass the compliance check for code generation.
Note: You cannot use the Simulink Coder keyboard short cut, Ctrl + B, to generate SimWB-compliant code.
You can use only the MLToolkit GUI to generate this code.
Run the Simulink Model in SimWB Control Center
Please click here to learn how to run the Simulink Model in real-time via SimWB Control Center.