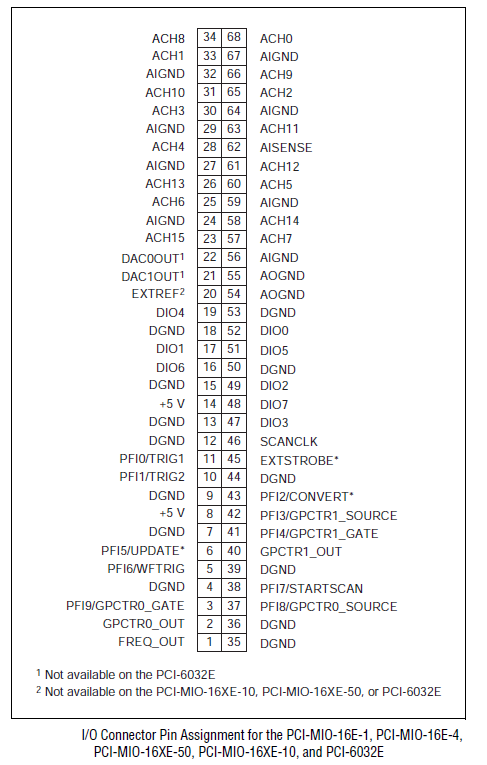
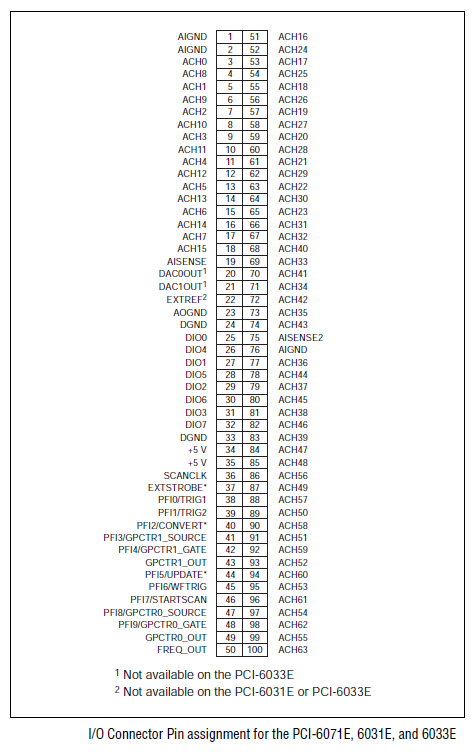
NI60xx boards are multifunction boards, providing varying numbers of analog input channels, analog output channels, bidirectional digital channels, and counters. See I/O Mappings... for generic information about mapping channels to I/O points. The left hand pane of the I/O Mappings form has separate tabs for analog channels, digital channels, and counters, each discussed separately below.
CS-NI-PCI-60xxE.
Included in SimWB.
ICS-SWB-1222.
Channel settings are stored with the I/O point mappings and will not persist if changed on a channel with no points mapped to it.

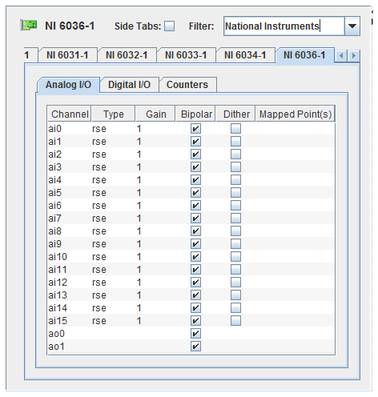
Name of the channel. The names of input channels are prefixed with ai, output channels with ao. The number of each varies with the board model.
Type of the input channel. To edit it, click on the value and select the new value from the drop down list. The choices are:
Referenced single ended. Also called “grounded referenced single ended,” the channel is referenced to the system ground.
Non-referenced single ended. The channel is referenced to a common point which is not grounded.
Differential. If N is the number of input channels, channel ai0 is referenced to channel aiN/2, channel ai1 to channel aiN/2+1, etc.
Amount of gain on the signal amplifier. To edit it, click on the value and select a new value from 0.5 to 100 from the drop down menu.
Selects between unipolar (0 to Vref) and bipolar (-Vref to Vref) input voltage ranges.
Selects adding approximately 0.5 LSBrms of white Gaussian noise to the signal.
I/O point(s) the channel is mapped to.
To map a point to a channel, select a channel on the left side of the I/O Mappings form, then click on a check box for an I/O point on the right side of the form. See I/O Mappings... for details.
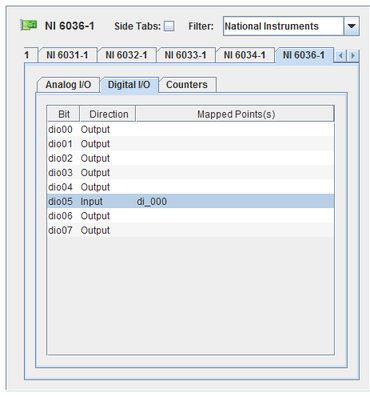
Name of the digital I/O channel.
Selects whether the digital channel is Input or Output. To edit it, click on the value and select a new one from the drop down list. Existing mappings will be removed when this value is changed.
I/O point(s) the digital I/O channel is mapped to.
To map a bit to a channel, select a bit on the left side of the I/O Mappings form, then click on a check box for an I/O point on the right side of the form. See I/O Mappings... for details.
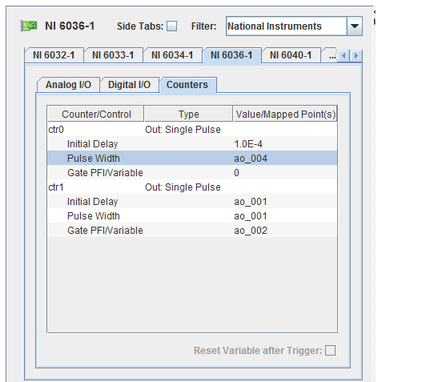
Counter or control of a output counter. Each control may have an point mapped to it. Most controls can be set to a constant value when no point is mapped to them.
Type of counter.
Output counters may be used as pulse generators in two modes:
Input counters may be used to take three different kinds of measurements:
Value of, or output point mapped to, a control of a output counter, or variable mapped to an input counter. Values may be edited by double clicking on them. Mappings are edited via the usual mechanism, by selecting a counter/control on the left side of the I/O Mappings form, then clicking on a check box for an I/O point on the right side of the form. See I/O Mappings... for details.
Generates a single pulse when triggered.
Delay in seconds between trigger and pulse.
Pulse duration in seconds.
Programmable function interface pin or output point that will be used to tigger the pulse. Set the variable to a non-zero value to have the output task generate a pulse during stage 4 of the test cycle.
Sets the output variable mapped to Gate PFI/Variable to be reset to zero after a pulse is generated.
Time in seconds between pulses.
Duration of the pulses in seconds.
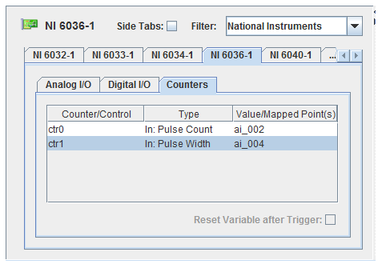
Measures the cumulative count of pulses.
Measures pulse widths in seconds.
Measures pulse period in Hz.
|
NET JOYSTICK | NI6509 |
|