This test simulates a plane flying on autopilot. As configured in the sample RTDB, it can make use of a joystick to control the flight. A joystick must be plugged into a USB port on the real-time host in order to run this test.
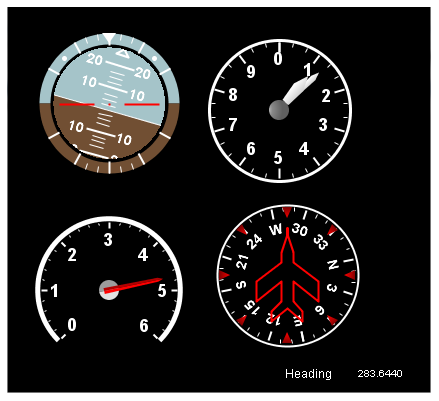
This display shows four flight-oriented instruments against a black background.

No background images are used to draw these. This is all SimWB drawing the widgets on a black background. A simulated autopilot is turning the plane to the right.
The Attitude Indicator widget (upper left) is connected to two I/O points that the model sets to the pitch and roll angles. The widget is inverting the display of the roll (this is a option that can be turned off in HMI Builder).
The two hands of the Altimeter widget (upper right) shows the altitude in thousands and hundreds of feet like a clock shows time in hours and minutes.
The tachometer is just a Gauge widget (lower left) as we saw in the autotrans test’s displays.
The heading is shown via a Heading Indicator widget (lower right). As an exercise, go to its Visual Properties and turn on and off the various components that can be shown or hidden.
As cool as the indicators look in the above display, using a photograph of an instrument panel to superimpose the widgets on provides an even better level of realism, as seen in the multigen2.swbd.

The background is just a photograph of an instrument panel with the centers of the instruments painted over to hide the original needles. The widgets then have their own scales disabled (for the most part) so that only the needle is used.

There is also an autopilot switch. Click on it to disengage the autopilot, then grab the joystick and play with climbing, diving and turning the plane.
|
Autotrans Test | rtdemo1 RTDB |
|